Thermal optimality and physiological parameters inferred from experimental studies scale latitudinally with marine speciesoccurrences
Abstract
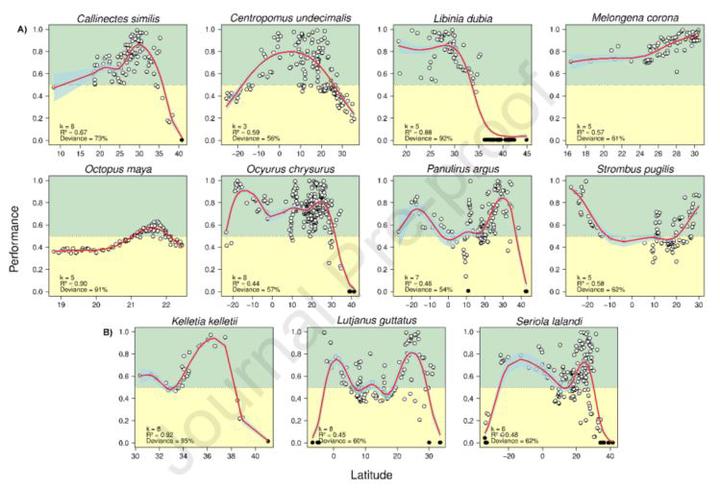
Ocean warming is expected to occur due to anthropogenic climate change bringing a spatial shift of marine communities. Experimental data that characterize the aerobic power budget via an aerobic scope (AS), thermal metabolic scope (TMS) approach, or thermal preferences have been proposed as tools that can describe species distribution since they characterize species fitness or performance under different temperatures. This study tested the potential relationship between observed occurrences and different physiological studies in the Americas for 11 commercially important species in Mexico. Projections were also developed for Mexico’s exclusive economic zone under different climate warming scenarios. The physiological data were fitted from optimum up to pejus temperatures and projected to sea surface temperatures for present (2003–2014) and Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) scenarios (RCP 2.6, RCP 4.5, RCP 6.0, and RCP 8.5) for the period 2040–2050 and 2090–2100. For species with wide distributions in the Americas, the number of occurrences reported decreases at higher latitudes related to the decrease in species performance calculated from laboratory experiments. In addition, higher species occurrences are usually reported around optimum temperatures. Overall, the results suggest that pejus temperatures likely restrict latitudinal distribution, at least for widely distributed taxons. Regarding Mexican projections, the results varied widely by species. For example, in the Atlantic Ocean, Octopus maya and Panulirus argus are vulnerable to warming scenarios, while those like Ocyurus chrysurus and Centropomus undecimalis are not. Interestingly, northern Campeche Bank, Gulf of California, and Western Baja California may act as thermal refugia for marine species indicating they could be assigned as protected areas to support fisheries throughout the Mexican exclusive economic zone. This research adds to the increasing evidence of the relationship between thermal niche and wild population distribution.